What is SWIR light?
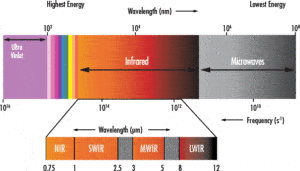
SWIR (Short-wave infrared) light is typically defined as light in the 0.9 – 1.7μm wavelength range, but can also be classified from 0.7 – 2.5μm. Since silicon sensors have an upper limit of approximately 1.0μm, SWIR imaging requires unique optical and electronic components capable of performing in the specific SWIR range. Indium gallium arsenide (inGaAs) sensors are the primary sensors used in SWIR imaging, covering the typical SWIR range, but can extend as low as 550nm to as high as 2.5μm.
Although linear line-scan inGaAs sensors are commercially available, area-scan inGaAs sensors are typically ITAR restricted. ITAR, International Treaty and Arms Regulations, is enforced by the government of the United States of America. ITAR restricted products must adhere to strict export and import regulations for them to be manufactured and/or sold within and outside of the USA. Nevertheless, lenses such as SWIR ones can be used for a number of commercial applications with proper licenses.
SWIR
WHY USE SWIR?
 Unlike Mid-Wave Infrared (MWIR) and Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR) light, which is emitted from the object itself, SWIR is similar to visible light in that photons are reflected or absorbed by an object, providing the strong contrast needed for high resolution imaging. Ambient star light and background radiance (nightglow) are natural emitters of SWIR and provide excellent illumination for outdoor, nighttime imaging.
Unlike Mid-Wave Infrared (MWIR) and Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR) light, which is emitted from the object itself, SWIR is similar to visible light in that photons are reflected or absorbed by an object, providing the strong contrast needed for high resolution imaging. Ambient star light and background radiance (nightglow) are natural emitters of SWIR and provide excellent illumination for outdoor, nighttime imaging.
It is essential to use a lens that is designed, optimized, and coated for the SWIR wavelength range. Using a lens designed for the visible spectrum will result in lower resolution images and higher optical aberrations. Since SWIR wavelengths transmit through glass, lenses, and other optical components (optical filters, windows, etc.) designed for SWIR light can be manufactured using the same techniques used for visible components, decreasing manufacturing cost and enabling the use of protective windows and filters within a system.
A large number of applications that are difficult or impossible to perform using visible light are possible using SWIR light. When imaging in SWIR light, water vapor, fog, and certain materials such as silicon are transparent. Additionally, colors that appear almost identical in the visible may be easily differentiated using SWIR light.
SWIR APPLICATIONS
SWIR imaging is used in a variety of applications including electronic board inspection, solar cell inspection, produce inspection, identifying and sorting, surveillance, anti-counterfeiting, process quality control, and much more. To understand the benefits of SWIR imaging, consider some visual examples of common, everyday products imaged with visible light and with SWIR light.
Short-wave infrared (SWIR) defines a specific wavelength range over which optical and electronic components are designed and coated. SWIR imaging offers a number of advantages compared to visible when used for inspection, sorting, surveillance, quality control, and host of other applications.
It is important to choose components specifically designed, optimized, and coated for the SWIR wavelength range to ensure the highest resolution and lowest aberrations. Manufacturers like SUPERIOR Optics are experienced in designing, manufacturing, and coating SWIR Series lenses. We offers lens assemblies designed with glasses that are optimized for performance in the SWIR spectrum, and anti-reflection (AR) coatings for SWIR light specially designed for maximum transmission of SWIR wavelengths.
Related Posts
What is SWIR Imaging?" rel="bookmark">What is SWIR Imaging?
How useful was this post? Click on a star to rate it! Submit Rating As you found this post useful......
What is SWIR Imaging Lenses?" rel="bookmark">What is SWIR Imaging Lenses?
How useful was this post? Click on a star to rate it! Submit Rating As you found this post useful......




